Page 10 - 10-phy-12 Geometrical Optics
P. 10
Experiment Determine the critical angle of glass
using a semi-circular slab and a light ray
12.3 box/ or by prism.
Date ________________
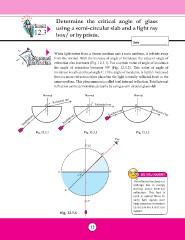
Background When light enters from a denser medium into a rarer medium, it refracts away
Information from the normal. With the increase of angle of incidence the value of angle of
refraction also increases (Fig. 12.3.1). For a certain value of angle of incidence
the angle of refraction becomes 90° (Fig. 12.3.2). This value of angle of
incidence is called critical angle C. If the angle of incidence is further increased
then no more refraction takes place but the light is totally reflected back in the
same medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. Total internal
reflection can be demonstrated clearly by using a semi circular glass slab
Normal Normal Normal Refracted ray
O r Refracted ray
O r Refracted ray O
i C Incident ray ir
Incident ray
Incident ray
Fig. 12.3.1 Fig. 12.3.2 Fig. 12.3.3
Q Eye
B¢
AO B
Ðc
DO YOU KNOW?
A¢ P
The reflected ray does not
Fig. 12.3.4 undergo loss in energy
during total internal
reflection. This fact is
used in optical fibres to
carry light signals over
large distances in modern
telecommunication
system.
12
using a semi-circular slab and a light ray
12.3 box/ or by prism.
Date ________________
Background When light enters from a denser medium into a rarer medium, it refracts away
Information from the normal. With the increase of angle of incidence the value of angle of
refraction also increases (Fig. 12.3.1). For a certain value of angle of incidence
the angle of refraction becomes 90° (Fig. 12.3.2). This value of angle of
incidence is called critical angle C. If the angle of incidence is further increased
then no more refraction takes place but the light is totally reflected back in the
same medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. Total internal
reflection can be demonstrated clearly by using a semi circular glass slab
Normal Normal Normal Refracted ray
O r Refracted ray
O r Refracted ray O
i C Incident ray ir
Incident ray
Incident ray
Fig. 12.3.1 Fig. 12.3.2 Fig. 12.3.3
Q Eye
B¢
AO B
Ðc
DO YOU KNOW?
A¢ P
The reflected ray does not
Fig. 12.3.4 undergo loss in energy
during total internal
reflection. This fact is
used in optical fibres to
carry light signals over
large distances in modern
telecommunication
system.
12