Page 18 - 10-phy-12 Geometrical Optics
P. 18
Experiment Find the focal length of a convex lens by
12.5 parallax method.
Date ________________
Background A lens is a part of a refractive medium OF
Information bounded by one or both curved surfaces.
There are two kinds of lenses
(i) Convex lens
(ii) Concave lens.
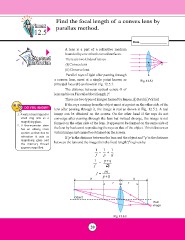
Parallel rays of light after passing through L
a convex lens, meet at a single point known as Fig. 12.5.1
principal focus (F) as shown in Fig. 12.5.1.
The distance between optical centre O of
lens and focus F is called focal length 'f'.
There are two types of images formed by lenses, (i) Real (ii) Virtual
DO YOU KNOW? If the rays coming from the object meet at a point on the other side of the
lens after passing through it, the image is real as shown in Fig. 12.5.2. A real
1. A water drop trapped in image can be obtained on the screen. On the other hand if the rays do not
small ring acts as a converge after passing through the lens but instead diverge, the image is not
magnifying glass. formed on the other side of the lens. It appears to be formed on the same side of
the lens by backward reproducing the rays as that of the object. This is known as
2. A thermometer stem virtual image and cannot be obtained on the screen.
has an oblong cross
section so that due to If 'p' is the distance between the lens and the object and ''q' is the distance
refraction it acts as between the lens and the image then the focal length 'f' is given by
magnifying glass and
the mercury thread 1= 1+ 1
appears magnified. f pij
1 = p+q
f ♫ij
f = pq q
p p+ij f
f
Object Real
image
20
Fig. 12.5.2
12.5 parallax method.
Date ________________
Background A lens is a part of a refractive medium OF
Information bounded by one or both curved surfaces.
There are two kinds of lenses
(i) Convex lens
(ii) Concave lens.
Parallel rays of light after passing through L
a convex lens, meet at a single point known as Fig. 12.5.1
principal focus (F) as shown in Fig. 12.5.1.
The distance between optical centre O of
lens and focus F is called focal length 'f'.
There are two types of images formed by lenses, (i) Real (ii) Virtual
DO YOU KNOW? If the rays coming from the object meet at a point on the other side of the
lens after passing through it, the image is real as shown in Fig. 12.5.2. A real
1. A water drop trapped in image can be obtained on the screen. On the other hand if the rays do not
small ring acts as a converge after passing through the lens but instead diverge, the image is not
magnifying glass. formed on the other side of the lens. It appears to be formed on the same side of
the lens by backward reproducing the rays as that of the object. This is known as
2. A thermometer stem virtual image and cannot be obtained on the screen.
has an oblong cross
section so that due to If 'p' is the distance between the lens and the object and ''q' is the distance
refraction it acts as between the lens and the image then the focal length 'f' is given by
magnifying glass and
the mercury thread 1= 1+ 1
appears magnified. f pij
1 = p+q
f ♫ij
f = pq q
p p+ij f
f
Object Real
image
20
Fig. 12.5.2