Page 2 - 9-phy-1 Measurements
P. 2
positive zero correction. For Fig 1.1.3,
Positive zero correction = + 0.06 cm
When the zero error is positive, it is subtracted from the observed reading to
obtain the correct value and is called negative zero correction. For Fig 1.1.2
Negative zero correction = – 0.03 cm
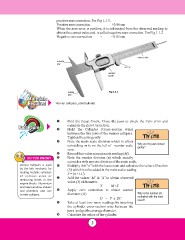
outside main scale
jaw screw
vernier
scale
inside Fig 1.1.4
jaw
Vernier callipers, solid cylinder.
ΠFind the Least Count. Close the jaws to check the Zero error and
calculate the Zero Correction.
Hold the Cylinder (Cross-section wise)
between the two jaws of the vernier callipers.
Tighten the jaws gently.
Ž Note the main scale division which is either Why are the jaws closed
gently?
coinciding or is on the left of vernier scale
zero.
Record this value as main scale reading (M).
Note the vernier division (n) which exactly
coincides with any one division of the main scale.
Vernier Callipers is used ‘ Multiply this “n” with the least count and calculate the value of fraction
by the lath mechanic for ’
making metallic cylinders “ (X) which is to be added in the main scale reading
of various sizes or
measuring bores in the X = (n × LC)
engine blocks. Aluminium
and Steel window makers Add the values ‘M’ & ‘X’ to obtain observed
and plumbers also use
vernier callipers. value (Y) of diameter.
Y = M+X
Apply zero correction to obtain correct
” diameter. (D) Why is the number (n)
D = Y ± ZC multiplied with the least
count?
Take at least two more readings by inserting
the cylinder cross-section wise between the
jaws and get the average diameter.
• Calculate the radius of the cylinder.
2
Positive zero correction = + 0.06 cm
When the zero error is positive, it is subtracted from the observed reading to
obtain the correct value and is called negative zero correction. For Fig 1.1.2
Negative zero correction = – 0.03 cm
outside main scale
jaw screw
vernier
scale
inside Fig 1.1.4
jaw
Vernier callipers, solid cylinder.
ΠFind the Least Count. Close the jaws to check the Zero error and
calculate the Zero Correction.
Hold the Cylinder (Cross-section wise)
between the two jaws of the vernier callipers.
Tighten the jaws gently.
Ž Note the main scale division which is either Why are the jaws closed
gently?
coinciding or is on the left of vernier scale
zero.
Record this value as main scale reading (M).
Note the vernier division (n) which exactly
coincides with any one division of the main scale.
Vernier Callipers is used ‘ Multiply this “n” with the least count and calculate the value of fraction
by the lath mechanic for ’
making metallic cylinders “ (X) which is to be added in the main scale reading
of various sizes or
measuring bores in the X = (n × LC)
engine blocks. Aluminium
and Steel window makers Add the values ‘M’ & ‘X’ to obtain observed
and plumbers also use
vernier callipers. value (Y) of diameter.
Y = M+X
Apply zero correction to obtain correct
” diameter. (D) Why is the number (n)
D = Y ± ZC multiplied with the least
count?
Take at least two more readings by inserting
the cylinder cross-section wise between the
jaws and get the average diameter.
• Calculate the radius of the cylinder.
2